Study ability concerns the entire university

Study ability is created through interaction between the student and the learning environment. This means that different actors in the higher education community can influence the progress of students in their own way. The study ability model describes factors affecting study ability from the student’s life situation to teaching policies and timetables to different study environments.
Study ability is the student’s work ability. It indicates how the student is able to develop and learn. Study ability is realised in the accumulation of study attainments and grades. It is concerning if one’s grades are dropping or there are no attainments.
Study ability is created through active interaction between the higher education institution and the students. This is why opportunities for interaction must be created continuously. High-quality teaching that activates students, with means such as group discussion exercises, also supports the student’s study ability.
The student’s ability to complete their studies depends on their own resources and study skills, the implementation of teaching and guidance, and the support received from the study environment. The study ability model developed by the Finnish Student Health Service and the Finnish Institute of Occupational Health (Figure 1) describes matters affecting study ability.
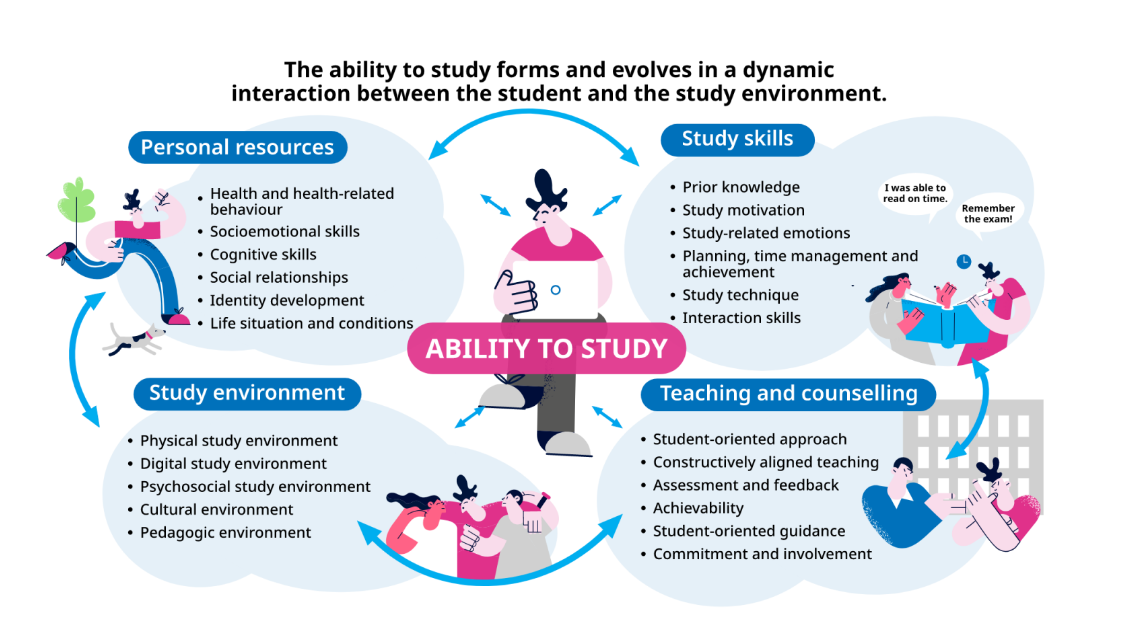
Figure 1 Study ability model [1]. The model is based on the model published by Kristina Kunttu (2006).
Areas of study ability
The students’ resources mainly consist of their own skills. Student health care can provide support in matters related to health, and the higher education institution can take the student’s life situation and circumstances into consideration by making individual arrangements. If necessary, the student may be allowed extended time for exams or additional time for submitting assignments. Alternative study methods or taking an exam in several parts may also support the completion of studies.
Issues affecting the student’s study skills can be considered in teaching, which should create confidence in the student’s own abilities. The higher education institution can support and maintain study motivation by, for example, creating opportunities for peer support and communality. Studying together supports the majority of students in a significant manner. Teaching practices that promote communal studies are important in building study ability and working life skills.
Each teacher and instructor can influence the student’s study ability through teaching and guidance. Higher education pedagogy that supports study ability is student-oriented. ‘Teaching and guidance should create safe, goal-oriented peer groups where students can reflect, share their experiences, knowledge and skills and support each other in learning.’ [1]
The timetable can be used to support students’ coping by distributing the load evenly throughout the week. At the same time, it will be possible for students to have time and opportunities for group work and independent study. The even distribution of study load within the semester requires co-operation between teachers.
Students and student organisations may be closely involved in building the study environment. It produces an experience of belonging to the study community and groups as well as participation, which is an essential part of the psychosocial study environment.
The role of the digital learning environment is growing. The clear structures of learning platforms help the student understand the big picture. When the deadlines for assignments are clearly visible to students on time, they do not unnecessarily burden the student’s memory. Getting teaching materials a few days before class may be important for some students. The above factors support students with learning difficulties in particular.
Peer groups and study ability
In the Study Group activities, the student has their own Study Group. The group carries out exercises related to studying together and supports and encourages each other. Through this, the student joins the higher education community and feels that they belong to the group. The group provides the student with a secure community for peer support. When working in a group, the student learns interaction and group work skills and sees how they learn the best.
By using the Study Groups in group work related to studying, scheduling and study ability can be facilitated. This is possible if the groups in different study units remain the same. This way, there is no need to agree on times with many different groups. In the group, students can reflect on their competence in a safe environment.
Peer groups organised for students in the same phase of studies, such as Valtti groups, help the students. The student gets peer support and notices that they are not alone: others can face similar challenges in their studies.
The entire higher education institution can have an influence
Study ability is created and developed through dynamic interaction between the student and the learning environment. All actors in the institution can contribute to this. Genuine encounters with students are important. Doing things together with other students supports your study ability.
Sinikka Viinikka, Lecturer, Oulu University of Applied Sciences, Information Technology
Susanna Saarinen, Lecturer, Oulu University of Applied Sciences, Social and Health Services
This article was published in Finnish 21.3.2023 in Oamk Journal.